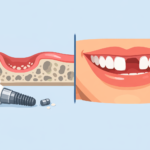
Implant abutments are crucial components in dental implant procedures. They act as connectors between the dental implant (which is surgically placed into the jawbone) and the final restoration, such as a crown or bridge. Abutments are typically made from materials like titanium or zirconia, known for their strength and biocompatibility.
The primary role of an abutment is to provide stability and support for the dental prosthetic. They come in various shapes and sizes to accommodate different implant systems and individual patient needs. Proper selection and placement of the abutment are essential for ensuring the long-term success of the dental implant.
- Connects the implant to the restoration.
- Available in multiple materials and designs.
- Ensures the stability of the dental prosthetic.
Types of Implant Abutments
Implant abutments come in various types, each designed to suit different needs in the dental restoration process. Generally, they can be classified into two main categories: prefabricated and custom abutments.
Prefabricated abutments are mass-produced and come in standard sizes and shapes. They are cost-effective and can be used for many patients with similar dental structures. Custom abutments, on the other hand, are specifically designed for an individual’s mouth, taking into account unique anatomical features. This customization allows for better fitting and improved aesthetic results.
- Straight abutments
- Angled abutments
- Platform-switching abutments
- Multi-unit abutments
Materials Used for Implant Abutments
Implant abutments can be made from several types of materials, each with its own benefits and considerations. The most common materials include:
- Titanium: Known for its strength and biocompatibility, titanium is a popular choice for dental abutments.
- Zirconia: This ceramic material is favored for its aesthetic appeal, as it can closely match the natural color of teeth.
- Gold: Gold abutments are durable and resistant to corrosion, but their visible color may be less desirable for some patients.
Choosing the right material for an implant abutment often depends on individual needs, preferences, and the specific circumstances of the patient’s dental health.
The Role of Implant Abutments in Dental Implants
Implant abutments serve as a critical connector between dental implants and the replacement teeth they support. Once the dental implant is placed in the jawbone, the abutment is attached to the implant, providing a stable base for crowns, bridges, or dentures.
The primary functions of implant abutments include:
- Creating a secure connection between the implant and the prosthetic teeth.
- Aiding in the proper alignment and positioning of the replacement teeth.
- Allowing for adjustments and modifications during the restoration process.
In essence, abutments play a vital role in ensuring that dental implants function effectively while mimicking the natural appearance of teeth.
How to Choose the Right Implant Abutment
Selecting the appropriate implant abutment is crucial for the overall success of your dental implant. Here are a few factors to consider:
- Material: Abutments can be made from titanium, zirconia, or other materials. Consider the benefits of each, such as strength and aesthetics.
- Compatibility: Ensure that the abutment is compatible with the specific implant system used by your dentist.
- Therapeutic Goals: Discuss your expected outcomes with your dentist to determine which abutment best supports those goals.
- Customization: Some cases might require custom abutments for better fit and alignment. Talk to your dentist about available options.
Ultimately, consulting with your dental professional is the best way to make an informed decision tailored to your needs.
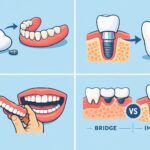
Benefits of Custom vs. Stock Implant Abutments
When it comes to choosing between custom and stock implant abutments, there are several factors to consider. Custom abutments are designed specifically for each patient, allowing for a more precise fit and improved aesthetic results. This customization can enhance the overall look of the dental restoration.
On the other hand, stock abutments are pre-manufactured and readily available. They can be a more cost-effective option and offer quicker treatment times. However, they may not provide the same level of fit and aesthetic appeal as custom abutments.
- Customization: Custom abutments can be tailored to individual anatomical features.
- Cost: Stock abutments are generally less expensive and accessible.
- Time Efficiency: Stock options can shorten the treatment duration.
Common Questions About Implant Abutments
Implant abutments are essential components that connect dental implants to the prosthetic teeth. Here are some frequently asked questions to help you understand them better:
- What is an implant abutment? An implant abutment is a small connector piece that attaches to the dental implant and supports the crown (the visible tooth).
- Are there different types of abutments? Yes, there are various types of abutments, including straight and angled options, and they can be made from different materials like titanium or zirconia.
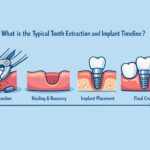
- How is an abutment placed? The abutment is typically placed after the dental implant has fused with the bone, and this process is done during a minor surgical procedure.
- Do implant abutments require special care? While they do not need special care, maintaining good oral hygiene is crucial for the longevity of the implant and abutment.
Maintenance and Care for Implant Abutments
Proper care and maintenance of implant abutments are essential for ensuring the longevity and functionality of your dental implants. Regular dental check-ups and an effective oral hygiene routine play a crucial role in preventing complications.
Here are some tips for maintaining your implant abutments:
- Brush your teeth at least twice a day with a soft-bristled toothbrush to remove plaque and debris around the abutment area.
- Floss daily to clean between your teeth and around the implant to prevent gum disease.
- Use an antimicrobial mouthwash to reduce bacteria and promote gum health.
- Visit your dentist regularly for professional cleanings and check-ups to monitor the condition of your implants and abutments.